
Authors: Zhao BW, Feng SL, Hu YX, Wang S, Lu XN
Article Title: Rapid determination of atrazine in apple juice using molecularly imprinted polymers coupled with gold nanoparticles-colorimetric/SERS dual chemosensor.
Publication date: 2019
Journal: Food Chemistry
Volume: 276
Page numbers: 366-375.
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.10.036
Alternative URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0308814618318028
Abstract: Rapid and reliable determination of atrazine, a common chemical contaminant, in agri-foods is highly necessary. We reported a novel dual-chemosensor coupling, a separation [molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs)], an instrumental-free detection [gold nanoparticles (AuNPs)-based colorimetric assay] and an instrument-based quantification [surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)] method for high-throughput and sensitive determination of atrazine in apple juice. Used as the selective sorbent for the solid phase extraction, MIPs effectively extracted atrazine from apple juice with high recoveries (~93%). AuNPs of different sizes (large; medium; and small) performed differently in the two analytical methods. Large-AuNPs provided the highest sensitivity in colorimetric analysis (<0.01 mg L-1), while medium-AuNPs achieved the lowest limit of detection (0.0012 mg L-1) and quantification (0.0040 mg L-1) in SERS analysis. With minor modifications, protocols for both analytical methods can rapidly detect and/or quantify atrazine in different food products complying with the Health Canada regulation (0.005 mg L-1)
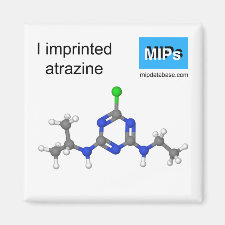
Template and target information: atrazine
Author keywords: Molecularly imprinted polymers, Colorimetric assay, Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy, chemosensor, atrazine, food safety


Join the Society for Molecular Imprinting

New items RSS feed
Sign-up for e-mail updates:
Choose between receiving an occasional newsletter or more frequent e-mail alerts.
Click here to go to the sign-up page.
Is your name elemental or peptidic? Enter your name and find out by clicking either of the buttons below!
Other products you may like:
 MIPdatabase
MIPdatabase









