
Authors: Men HF, Liu HQ, Zhang ZL, Huang J, Zhang J, Zhai YY, Li L
Article Title: Synthesis, properties and application research of atrazine Fe3O4@SiO2 magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer.
Publication date: 2012
Journal: Environmental Science and Pollution Research
Volume: 19
Issue: (6)
Page numbers: 2271-2280.
DOI: 10.1007/s11356-011-0732-9
Abstract: Introduction Magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles were prepared by coprecipitation and then were coated with SiO2 on the surface. Materials and methods Fe3O4@SiO2 composite microspheres were modified by KH570. Using molecular imprinting technology, atrazine magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer was prepared by using atrazine as template molecule, methacrylic acid as functional monomer and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as cross-linkers. The morphology, composition and magnetic properties of magnetic nanoparticles were characterized. The recognition selectivity of polymer was studied for template molecule and simulation by UV spectrophotometry. The adsorption properties and selectivity ability were analyzed by Scatchard analysis. Results Scatchard linear regression analysis indicated that there are two binding sites of the target molecules. The magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer has been applied to the analysis of atrazine in real samples. Conclusion The results show that: the recovery rates and the relative standard deviation were 94.0 - 98.7% and 2.1 - 4.0% in corn, the recovery rates and the relative standard deviation were 88.7 - 93.5% and 2.8 - 7.2% in water
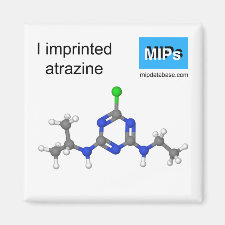
Template and target information: atrazine
Author keywords: atrazine, Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer, Fe3O4@SiO2, Selectivity ability


Join the Society for Molecular Imprinting

New items RSS feed
Sign-up for e-mail updates:
Choose between receiving an occasional newsletter or more frequent e-mail alerts.
Click here to go to the sign-up page.
Is your name elemental or peptidic? Enter your name and find out by clicking either of the buttons below!
Other products you may like:
 MIPdatabase
MIPdatabase









