
Authors: Liu JB, Sun JN, Tang SS, Chen KY, Jin RF
Article Title: Theoretical researches on the recognizing characteristics of atrazine imprinted polymers with different functional monomers.
Publication date: 2012
Journal: Chinese Journal of Structural Chemistry
Volume: 31
Issue: (12)
Page numbers: 1794-1802.
Alternative URL: http://www.jstructchem.cn/qikan/epaper/zhaiyao.asp?bsid=15480
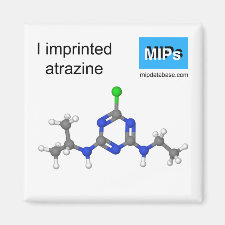
Abstract: As a widely used herbicide, the threat of atrazine to both environment and health of people has become the focus. Therefore, the research and analysis of atrazine are getting more important. In this work, the MIT was used to detect atrazine theoretically. Atrazine was taken as a template molecule. MAA, MMA and TFMAA were taken as the functional monomers, respectively. The geometry optimization, the nature of hydrogen bonds, the NBO charge, and the binding energies of the imprinted molecule with the functional monomers were investigated at the B3LYP/6-31g(d,p) level. Results indicated that atrazine had the strongest interaction with TFMAA. When the ratio of atrazine and TFMAA was 1:6, the amount of H-bond formed from atrazine and TFMAA was the largest. Moreover, TFMAA owned the largest binding energy with atrazine while MMA owned the smallest. The study is helpful to interpret experiment phenomena of molecular imprinting and select better functional monomers
Template and target information: atrazine
Author keywords: atrazine, Density functional theory, hydrogen bonds, molecular-imprinted polymer


Join the Society for Molecular Imprinting

New items RSS feed
Sign-up for e-mail updates:
Choose between receiving an occasional newsletter or more frequent e-mail alerts.
Click here to go to the sign-up page.
Is your name elemental or peptidic? Enter your name and find out by clicking either of the buttons below!
Other products you may like:
 MIPdatabase
MIPdatabase









